- Main page
- Search
- Up to date
- Products
- Technology
- Vehicles
- Video
- Conversion Payback Simulator
Port Injection - Conversion Payback Simulator
Direct Injection - Conversion Payback Simulator
Diesel - Newsletter
Flexible hoses in autogas systems
 loading results...
loading results... © gazeo.com
© gazeo.com
Flexible LPG hoses are also used for connecting autogas injectors with nozzles located in the intake manifolds. In any case, LPG is in its vapour state and at low pressure, but even though, hoses used for autogas systems are designed particularly for this kind of use and must undergo complex certification procedures as detailed in the 67 EEC UN regulation. The regulation takes into consideration the specific conditions under which the LPG hoses operate in a vehicle converted to run on autogas.
Pressure and temperature
The 67 regulation specifies LPG hoses as low-pressure rubber hoses, which must withhold a maximum working pressure of 4,5 bars (0,45 MPa) while used within the -25 to 125° C scope of temperatures. Should need arise to certify hoses to work in temperature conditions outside this range, certification procedures are adjusted accordingly (as specified in the 67 regulation).
Build of the LPG hose
According to the requirements of the regulation, low-pressure must consist of a smooth-walled internal hose and an external jacket with at least one reinforced protection layer in between. If the protection layer's reinforcement is made of non-corrosive material, the jacket is not required.
The internal part
The internal hose has physical contact with flowing LPG, so the choice of rubber mixture of which this part is to be made must take into consideration the specifics of the fuel. First and foremost, the rubber must be resistant to hydrocarbons.
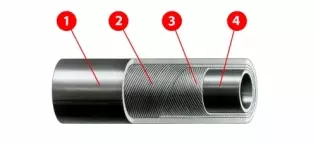 © Parker HanifinStructure of an LPG hose: 1 - external layer with high mechanical (attrition, cuts) and chemical (hydrocarbons) resistance; 2, 3 - reinforcement made of durable fibres; 4 - chemically resistant internal rubber hose
© Parker HanifinStructure of an LPG hose: 1 - external layer with high mechanical (attrition, cuts) and chemical (hydrocarbons) resistance; 2, 3 - reinforcement made of durable fibres; 4 - chemically resistant internal rubber hoseReinforcement
As said above, LPG hoses feature reinforcements. Thanks to them hoses retain their internal flow diameters even despite bending and remain resistant to internal pressure. Various fibres are used for reinforcements, including textile, artificial and metal ones. Aramid fibres work particularly well due to their high resistance to high temperatures.
External layer (jacket)
This is the part protecting the hose from the conditions of the engine bay environment, such as temperature, oil (and other lubricants) and various engine liquids in general. The jacket also protects the hose mechanically from damage.
Materials
In the process of LPG hose production various synthetic rubber mixtures containing appropriate additional ingredients are used. It's the additions that determine particular specifics of a given hose, so no wonder they are kept secret by hose manufacturers. For hoses used in motor fuel systems (including LPG) NBR and CSM rubbers are used, since they expose exceptional resistance to the influence of hydrocarbons.
 © gazeo.comThe connection between the reducer and the vapour state LPG filter is one example of use of rubber hoses
© gazeo.comThe connection between the reducer and the vapour state LPG filter is one example of use of rubber hosesStructural durability
The internal tube and the reinforcement must expose stretching resistance up to 10 MPa and be able to stretch by at least 250% in total, according to the ISO 37 standard. The reinforced jacket is subject to the same mechanical durability requirements as the internal tube.
Furthermore, LPG hoses are tested in terms of resistance to bending. A 3,5 m piece of hose is placed in a special test bench and should withstand 3000 repeated bends without breaking. Once the mechanical bending test is complete, the same piece of hose is subject to 1,015 MPa (10,15 bars) internal pressure for 10 minutes, during which time it shouldn't show signs of deteriorated tightness. Burst pressure value for the hose must be at least 1,8 MPa (18 bars).








